In fiber optic cable market, the demand for single mode fiber and multimode fiber optic cable are increasing rapidly. Both of them are available for higher bandwidth and faster speed connections. Between them, multimode fiber is commonly used for shorter distance data transmission in LAN enterprise and data center applications. However, how much do you know about multimode fiber? Let’s have an overview of multimode fiber in this article.
What is Multimode Fiber
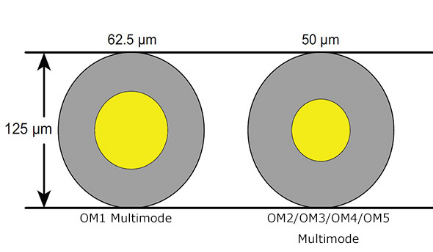
Multimode fiber (MMF) is a kind of optical fiber commonly used in communication for relatively short distances, for instance, inside buildings or corporate campuses. Multimode fiber optic cable has a larger core, typically 50 or 62.5 microns that enables multiple light rays or modes to be propagated simultaneously. However, the modes tend to disperse over longer lengths that the transmission distance of MMF is limited. The maximum transmission distance for MMF cable is around 550m at 10Git/s. Other typical transmission and distance limits are 2km at the speed of 100Mb/s and 1km at 100Mb/s.
Multimode Fiber Types
Multimode fiber optic cables can be categorized into OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5 fiber types by ISO 11801 standard. The next part will compare these fibers from the side of core size, bandwidth, data rate, distance, color and optical source in details.
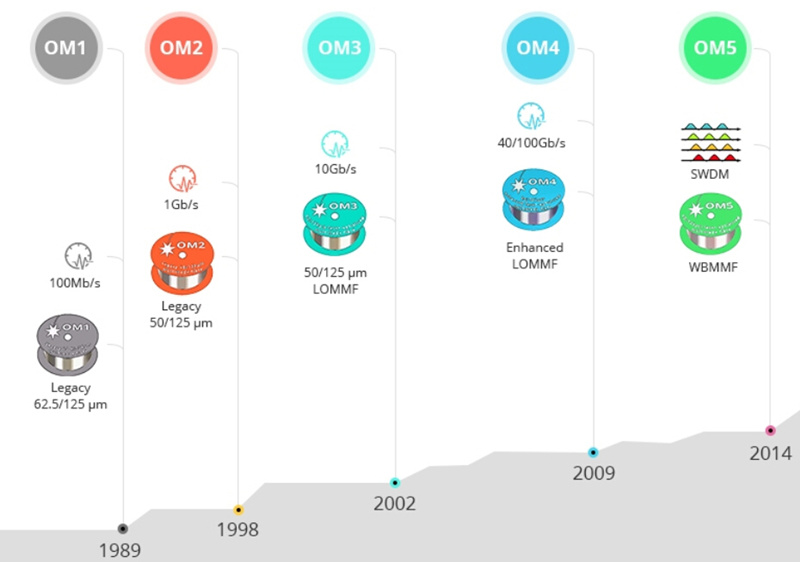
Initially OM1 fiber typically comes with an orange jacket and has a core size of 62.5 micrometers (µm). It can support 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths of up to 33 meters. It is most commonly used for 100 Megabit Ethernet applications. This type is suited for using a LED light source.
Conventional OM2 has a suggested jacket color of orange and works with LED based equipment as well as OM1. While it has a smaller core size of 50µm instead of 62.5µm. It supports up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 82 meters, but is more commonly used for 1 Gigabit Ethernet applications.
OM3 comes with an aqua color jacket. Like the OM2, its core size is 50µm, but the cable is optimized for laser based equipment. OM3 provides 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 300 meters, which is its most common use. Moreover, this type enable its use with 40 Gigabit and 100 Gigabit Ethernet up to 100 meters.
OM4 is completely a further improvement to OM3. They share the same distinctive aqua jacket, same core size of 50µm and both of them are optimized for laser based equipment. But OM4 supports 10 Gig/s at lengths up to 550 meters and it supports 100 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 150 meters.
OM5 fiber, also known as WBMMF (wideband multimode fiber), is backwards compatible with OM4. It has the same core size as OM2, OM3, and OM4. The official color of OM5 fiber jacket is lime green. It is designed and specified to carry at least four WDM channels at a minimum speed of 28Gbps per channel through the 850-953 nm window.
OM1 VS OM2 VS OM3 VS OM4 VS OM5:What’s the Difference
The primary difference between these types of multimode fibers depends on physical difference. Correspondingly, physical difference results in various transmission data rate and distance. The following part are their essential distinctions from physical and practical aspect.
Physical difference mainly lies in diameter, jacket color, optical source and bandwidth, which is exposed in the following figure.
|
MMF Cable Type
|
Diameter
|
Jacket Color
|
Optical Source
|
Bandwidth
|
|
OM1
|
62.5/125µm
|
Orange
|
LED
|
200MHz*km
|
|
OM1
|
50/125µm
|
Orange
|
LED
|
500MHz*km
|
|
OM3
|
50/125µ
|
Aqua
|
VSCEL
|
2000MHz*km
|
|
OM4
|
50/125µm
|
Aqua
|
VSCEL
|
4700MHz*km
|
|
OM5
|
50/125µm
|
Lime Green
|
VSCEL
|
28000MHz*km
|
The chart below illustrates the maximum reach of Ethernet variants over different types of multimode fiber.
|
MMF Category
|
Fast Ethernet
|
1GbE
|
10GbE
|
40GbE
|
100GbE
|
|
OM1
|
2000m
|
275m
|
33m
|
/
|
/
|
|
OM2
|
2000m
|
550m
|
82m
|
/
|
/
|
|
OM3
|
2000m
|
/
|
300m
|
100m
|
70m
|
|
OM4
|
2000m
|
/
|
550m
|
150m
|
150m
|
|
OM5
|
/
|
/
|
550m
|
150m
|
150m
|
The Advantages of Multimode Fiber
Although multimode fiber has distance limits, it still has many significant advantages.
- Multimode fiber can support multiple data transfer protocol, including Ethernet, Infiniband, and Internet protocols.
- Multimode fiber carries multiple signals concurrently in the same line. Besides, the total power inside the signals carries almost no loss. Therefore, multimode fiber generally is utilized for backbone applications in buildings.
- Last but not the least, MMF and components are cost effective and are easier to work with other optical components like fiber adapter and various fiber connectors, and multimode patch cords are less expensive to operate, install and maintain.
Conclusion
In general, multimode fiber cable continues to be the most cost-effective choice for enterprise and data center applications with 500-600 meter range. As for whether to choose a single mode fiber or multimode fiber, the applications that you need, transmission distance to be covered as well as the overall budget should be taken into consideration.




