Today, with the requirements of the bandwidth, many data centers use 40G Ethernet for connectivity from their servers to their top-of-rack switches. Most Hyperscale public cloud providers and social media giants are even migrating to 100G Ethernet for their servers in the near future. However, for some proactive enterprises, they are finding a cost effective and power efficient solution – 25G Ethernet is the answer to this challenge. Indeed, a handful of powerful data center and cloud vendors and suppliers, such as Google, Microsoft, Broadcom, Arista and Mellanox, formed a consortium to promote and catalyze development of 25G in 2014. You may have heard plenty of buzz regarding 25G Ethernet. What is 25G? Why 25G? Let’s take a closer look.

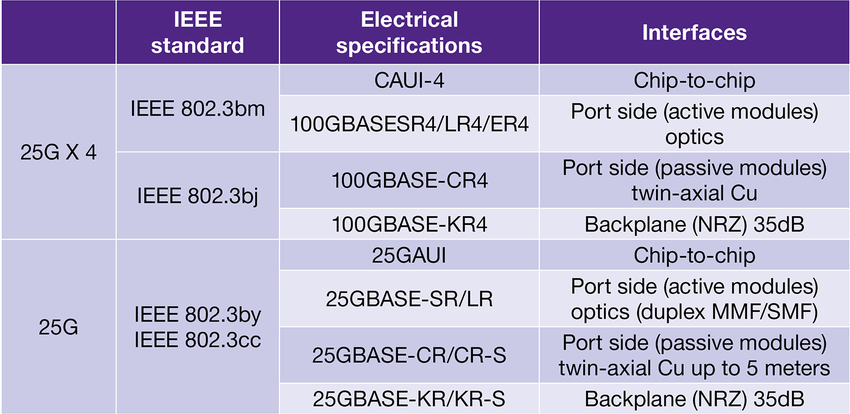
25G is a proposed standard for Ethernet connectivity that could benefit cloud and enterprise data center environments. In June 2014, the IEEE explored the standardization of 25G Ethernet. Subsequently, the standards organization has formed an 802.3by 25G Ethernet study group. They focus on market opportunities and requirements for a single-lane 25G Ethernet speed for server interconnects. Ethernet 25G is an emerging network technology, which is mainly used for the next generation of data center server. Ethernet 25G can provide a 25G media access control (MAC) that matches the single-lane 25G physical layer (PHY) technology. In web-scale data centers, 25G could provide an efficient server to increase top-of-rack (TOR) speed. That 25G technology can save cloud providers and enterprise data centers capital and operating expense.
Before 25G Ethernet exists, the only available option for higher speed server connectivity is 40G Ethernet. When top-of-rack switches move to high-density 40G Ethernet, the switches could still be connected to 10G servers, because 40G Ethernet consists of four lanes of 10G. And now, there are not only 40G standard under the way, but also the 25G Ethernet standards can be used to build a single-lane 25G Ethernet connection, a 2 x 25G configuration for 50G Ethernet or a 4 x 25G configuration for 100G Ethernet. With the availability of 4 x 25G per lane technology for 100G, a single 25G lane can reduce cost in comparison to 40G based on four 10G lanes. So 25G Ethernet technology is ready now.
Cloud computing is the most biggest attractions for Ethernet 25G. Cloud providers are looking forward to reducing cost and improving density, but 10G is no longer the need of server speeds. Under this condition, 10G requires more switches in the rack, so it needs higher cost. With the emergence of 25G technology, the IEEE has defined 100G Ethernet based on four lanes each at 25G. With the success of 100G Ethernet in data center networks for inter-switch links, Ethernet 25G has proven to be a reliable and cost effective technology. And Dell’Oro Group predicts that 25G will take over Ethernet server port sales by 2018.
Since the 25G Ethernet Consortium was formed in 2014, multiple suppliers have released silicon and system products that support the standard. Major server vendors offer 25G, 50G and 100G Ethernet adapters, while a broad range of switch vendors support 25G, 50G and 100G Ethernet speeds. In addition, the latest merchant silicon switches deliver up to 32 ports of 100G with single lane SerDes architectures with 128 lanes of 25G, making 25G a logical speed choice for migration of next generation server and storage. Therefore, there are 25G Ethernet solutions from all of the major switch and server vendors. As more and more of the server, switch and storage infrastructure converts to 25G, you will be able to recognize the performance and efficiency of the faster network speeds.
25G solutions provide 2.5x more bandwidth, but they are not significantly more expensive than 10G Ethernet solutions. Furthermore, they are fully backwards compatible when connected to 10G equipment. When you upgrade data center network to 25G, you can refresh your network with 25G capabilities instead of upgrading the whole system. Compared with 40G solutions, the underlying technology for 40G Ethernet is simply four lanes at 10G speed. It does not offer the advantages of cost, power consumption and server rack density, which enable widespread speed transition. All in all, 25G Ethernet provides lower costs and power requirements, which can enable network bandwidth to be cost-effectively and support the next-generation server and storage solutions in cloud and web-scale data center environments.
25G Ethernet leverages the single-lane 25G physical layer technology to support 100G Ethernet, which offers higher speed, lower power consumption and lower cost. In the near future, 25G Ethernet deployments will become the highest server port deployment. You can be ready for 25G and begin seeing the benefits of better compute and storage efficiency in your data center today.




