Optical amplifier, with the introduction in the 1990s, conquered the regenerator technology and opened doors to the WDM technology. It is mainly used to amplify an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. There are many types of optical amplifiers, namely Raman amplifiers, erbium doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs), and semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA). This article will make a clearer introduction to SOA amplifier, and analyze its advantages and disadvantages.

The Basics of Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA)
SOA optical amplifiers use the semiconductor as the gain medium, which is designed to be used in general applications to increase optical launch power to compensate for the loss of other optical devices. Semiconductor optical amplifiers are often adopted in telecommunication systems in the form of fiber-pigtailed components, operating at signal wavelengths between 0.85 µm and 1.6 µm and generating gains of up to 30 dB. Semiconductor optical amplifier, available in 1310nm, 1400nm, 1500nm, 1600nm wavelength, can be used with single mode or polarization maintaining fiber input/output.
Key Points of SOA Amplifier
- 1310 nm, 1400 nm, 1550 nm and 1610 nm wavelength selectable
- A high fiber-to-fiber gain of 20 dB
- Up to 16 dBm output
- 1 MHz with 10 ns pulse width (optional)
- PM Panda fiber input/output (optional)
- Similar to lasers, but with non-reflecting ends and broad wavelength emission
- Incoming optical signal stimulates emission of light at its own wavelength
- The process continues through the cavity to amplify the signal
Working principle of SOA amplifier
The basic working principle of an SOA is the same as a semiconductor laser but without feedback. SOAs amplify incident light through stimulated emission. When the light traveling through the active region, it causes these electrons to lose energy in the form of photons and get back to the ground state. Those stimulated photons have the same wavelength as the optical signal, thus amplifying the optical signal.
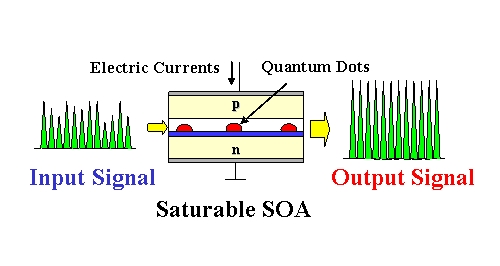
SOA Over EFDA in DWDM Networks
As the solution below, 120km Metro Networks by Using an SOA amplifier. You may wonder why not use EDFA in the above networks.
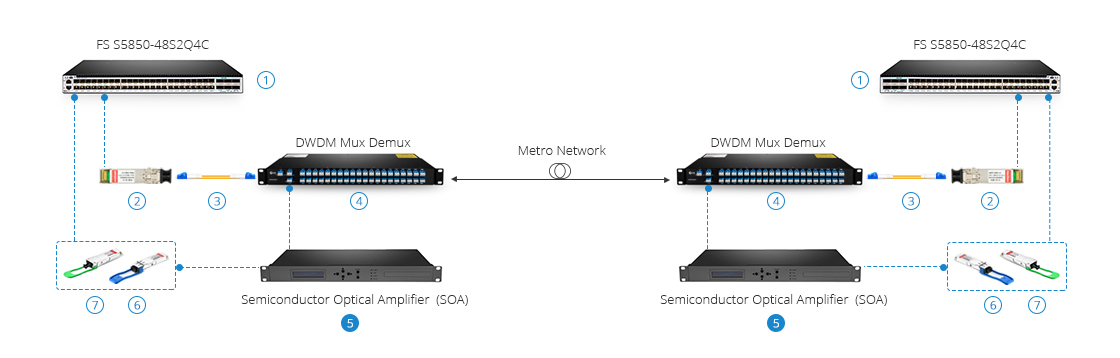
| Item No. | ID# | Description |
| 1 | 29124 | S5850-48S2Q4C (48*10GE+2*40GE+4*100GE) Carrier Grade 100G-uplink Switch |
| 2 | 31238 | 10G DWDM SFP+ C21-60 80km DOM Transceiver |
| 3 | 40191 | 1m LC UPC to LC UPC Duplex 2.0mm PVC 9/125 Single Mode Fiber Patch Cable |
| 4 | 35887 | 40 Channels C21-C60 Dual Fiber DWDM Mux Demux, with 1310nm Port for 40G/100G LR4 |
| 5 | 35192 | 10dB Gain 1310nm Semiconductor Optical Amplifier |
| 6 | 24422 | 40G QSFP+ LR4 1310nm 10km, LC Duplex Interface |
| 7 | 65219 | QSFP28 100GBASE-CWDM4 1310nm 2km Transceiver |
Theoretically, SOA optical amplifiers are not comparable with EDFA in terms of performance. The noise figure of SOA optical amplifier is typically higher, the gain bandwidth can be similar, SOAs exhibit much stronger nonlinear distortions in the form of self-phase modulation and four-wave mixing. Yet, the semiconductor optical amplifier is of small size and electrical pumped, which is often less expensive than EDFA. Additionally, SOA can be run with a low power laser.
How to Choose SOA Optical Amplifier?
When selecting SOA amplifier, you have to check every detailed parameter in the product data sheet. But, seriously, do you understand it? No, please read the following part.
The key parameters used to characterize an SOA amplifier are gain, gain bandwidth, saturation output power, and noise.
Gain is the factor by which the input signal is amplified and is measured as the ratio of output power to input power (in dB). A higher gain results in higher output optical signal.
Gain bandwidth defines the range of bandwidth where the amplification functions. A wide gain bandwidth is desirable to amplify a wide range of signal wavelengths.
Saturation output power is the maximum output power attainable after amplification beyond which no amplification is reached. It is important that the SOA has a high power saturation level to remain in the linear working region and to have higher dynamic range.
Noise defines the undesired signal within the signal bandwidth which arises due to physical processing in the amplifier. A parameter called noise figure is used to measure the impact of noise which is typically around 5dB.
Conclusion
SOA amplifier is the economic, high-performance solution for long-haul WDM networks. SOA amplifier, due to its features, can be used in Booster and in-line amplification, an optical network, general purpose test, and measurement and fiber sensing. However, it also has its limitations. In semiconductor optical amplifiers, electron-hole recombination occurs which will affect the performance of the whole line. FS offers EDFA, SOA, Raman optical amplifiers of excellent quality and price. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us.
Related article:
Optical Amplifier – EDFA (Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifier) for WDM System
How Does Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) Benefit WDM Systems




