Recently, it is increasingly obvious that fiber optic cable is replacing the copper cable as a communication way step by step. One reason is that fiber optic cable can extend the distance of local phone systems and network systems, including university campuses, office buildings, industrial plants, and electric utility companies. In addition, current fiber optic cable is capable of operating at an astounding speed to meet the ever-growing demands of business infrastructure. In this article, we are going to illustrate the fiber optic cable speed, which involves the speed introductions of single mode fiber and multimode fiber.
Fiber Optic Cable Speed Introduction
Fiber optic cable contains strands of optically pure glasses. For the glasses, they are thinner than a human hair and can carry digital information over a long distance. Digital signals are sent as pulses of light without interference or limitation. In that way, the digital transport system is faster and more reliable. Fiber optic technology allows for more data to be transferred in a shorter time than the older internet technology, like cable and DSL. For internet users, the higher data rate will lead to faster fiber optic cable speed, higher-quality streaming, and a better internet experience.
Single Mode and Multimode Fiber Optic Cable Speed Introduction
Fiber optic cable comes in two types: single mode fiber and multimode fiber. Under these two types, there are many sub-branches, such as the single mode LC fiber for long distance transmission and the multimode LC fiber for short distance transmission. However, for different types of cables, they have corresponding fiber optic cable speed as well.
- Single Mode Fiber Optic Cable Speed
Single mode cable is a single strand of glass fiber with a relatively narrow diameter, about 8.3 to 10 microns. Usually, it has one mode of transmission that propagates at the wavelength of 1310nm and 1550nm. On that account, there will be little light reflection when the light passes through the single mode fiber core. Consequently, it will reduce fiber attenuation and optimize the speed for the transmitting signals. For single mode fiber optic cable speed, no matter data rate is at 100 Mbit/s or Gbit/s, the transmission distance can reach up to 5 km. In that case, it is usually used for long distance signal transmission.
- Multimode Fiber Optic Cable Speed
Multimode fiber is made of glass fiber with a diameter size from 50 to 100 microns. With a larger core, it can guide many modes simultaneously. This gives rise to the more data transit through the multimode fiber core. Moreover, it will bring higher light reflection, dispersion, and attenuation rates. Multimode fiber provides higher bandwidth at higher fiber optic cable speed. It is mostly used for short distance communication, such as within a building or on a campus. Typically, the multimode fiber optic cable speed and the transmitting distance limits are 100 Mbit/s for distance up to 2 km (100BASE-FX), Gbit/s up to 1000m, and 10 Gbit/s up to 550 m.
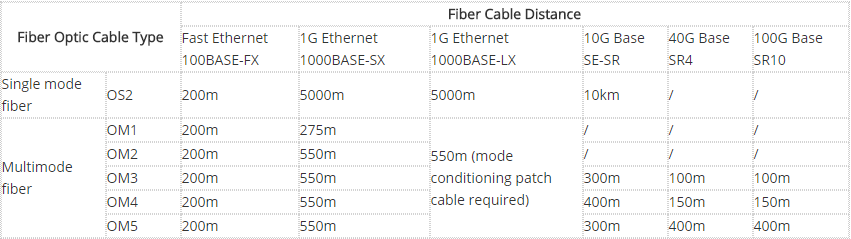
The following chart lists the transmission distance of SMF and MMF at different fiber optic cable speeds:
Conclusion
Fiber optic cable is the fastest mode of broadband technology available today. It sets an excellent example for businesses which are looking forward to optimize their system performance with higher bandwidth. In general, single mode fiber with a much smaller core gives you a higher transmission rate than multimode fiber. From this article, you would have a deeper understanding about fiber optic cable speeds for both single mode fiber and multimode fiber. If you have any need in this respect, FS.COM will always be your good choice.
Related Articles: