SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) is designed to meet Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) standards to ensure network equipment compatibility. Recently, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) technology is warmly welcomed by internet users all around the world. It is a technology that multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals at different wavelengths of laser light over a single optical fiber. By using WDM technology, SFP modules will have different wavelengths assigned to them. The following passage will focus on the brief descriptions of the two types of SFP modules: DWDM vs CWDM.
Overview of CWDM SFP
CWDM SFP is a kind of optical transceiver that utilizes CWDM technology. Similar with traditional SFP module, the CWDM SFP is a hot-swappable input/output device. It plugs into an SFP port or slot of a switch or router and links the port with the fiber-optic network. CWDM SFP transceiver modules make use of the SFP interface for connecting the equipment and use dual LC/PC fiber connector interface for connecting the optical network. Colorful CWDM SFP modules are displayed below.

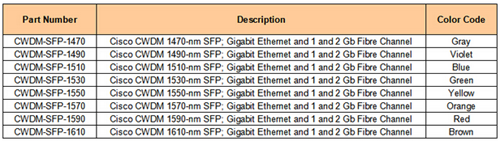
It is well known that CWDM SFP modules come in 8 wavelengths covering from 1470 nm to 1610 nm. Color markings on the devices identify the wavelength to which the Gigabit Ethernet channel is mapped. The following picture lists the CWDM SFPs with their wavelengths and color codes.
DWDM SFP Overview
DWDM (Dense Wavelength-Division Multiplexing) SFP transceivers are used as part of a DWDM optical network to provide high-capacity bandwidth across an optical fiber network, which is a high performance, cost-effective module for serial optical data communication applications up to 4.25Gb/s. There are 32 fixed-wavelength DWDM SFPs that support the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) 100-GHz wavelength grid. An inner structure of DWDM SFP is shown below.
Application
CWDM SFP transceiver is widely used in optical communications for both telecommunication and data communication. It is designed for operations in Metro Access Rings and Point-to-Point networks using Synchronous Optical Network (SONET), SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy), Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel networking equipment. The DWDM SFP can be also used in DWDM SONET/SDH (with or without FEC), but for longer transmission distance like 200km links and Ethernet/Fibre Channel protocol traffic for 80km links.
Which SFP Module Type Should You Choose: DWDM vs CWDM?
From a low-cost point of view, the CWDM SFP module is inexpensive than DWDM SFP. It provides a convenient and cost-effective solution for the adoption of Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel. On the other hand, the key in selecting DWDM vs CWDM SFP modules lies in the differences between CWDM and DWDM. They refer to different methods of splitting up the light. For example, CWDM uses broader spacing between channels, allowing for inexpensive SFPs, and DWDM uses denser channel spacing, which allows for more wavelengths to be used on a single fiber. DWDM is typically used in large optical networks over the longer distance. Thus if you are looking for SFP modules over long distance and with better scalability, DWDM SFP module is the ideal choice.
Conclusion
I hope this brief introduction to DWDM vs CWDM SFP modules is helpful for you to make a choice in selecting them. Based on the Cisco CWDM SFPs, FS CWDM SFPs are multi-rate transceivers, supporting data rates from 100 Mbps up to 4 Gbps. Besides, they support transfer distance at 20-40km, 40-80km and 80-120km in different colors, diversely satisfy the requirements of clients. All the DWDM SFP modules meet the requirements of the IEEE802.3 Gigabit Ethernet standard. They are suitable for interconnections in Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel environments.
Related Articles:




